India has become the fourth most equal society in the world.
This means that the benefits of the country's development are reaching the maximum number of people.
World Bank Latest Report – This information has come to light through the Gini Index.
In this list, India ranks above 167 countries and is positioned just below Slovakia, Slovenia, and Belarus.
 |
| Social News In Rajasthan |
Let’s understand the significance of this report through 6 questions and answers...
Question 1: What does it mean to be one of the most equal societies in the world?
Answer: India ranks fourth among the countries in the world where income is distributed most equally. This means the economic gap between the rich and the poor in India has reduced compared to earlier.
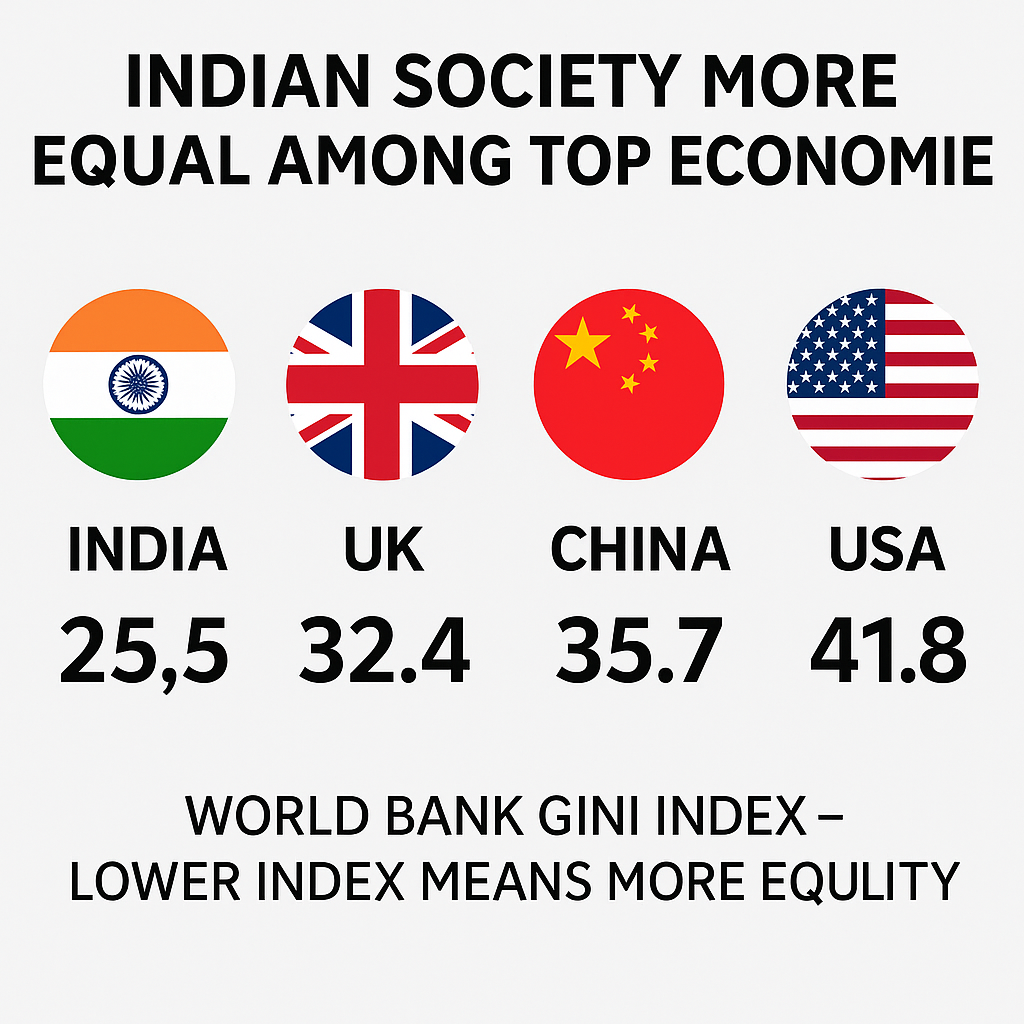
India's Gini Index is 25.5, which indicates low economic inequality in the country. This score comes just after Slovakia, Slovenia, and Belarus. However, it is better than that of China (35.7), the United States (41.8), and even the G7 and G20 countries.
Question 2: What is the Gini Index?
Answer: The Gini Index is a type of equality measurement that indicates how evenly income or wealth is distributed in a country. The score ranges from 0 to 100—where 0 means perfect equality (everyone has the same income), and 100 means perfect inequality (all income is held by just one person).
India's score is 25.5, which falls under the category of "moderately low" inequality. In 2011, it was 28.8, meaning India has made significant progress toward equality in recent years.
 |
| Social News In Rajasthan |
Question 3: How did India achieve this?
Answer: India achieved this through several government schemes and policies. For example:
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana: Over 550 million bank accounts were opened, connecting the poor to the banking system.
Aadhaar: More than 1.42 billion people were given a digital identity, enabling direct transfer of government benefits to their bank accounts. This has saved ₹3.48 lakh crore.
Ayushman Bharat: This scheme provided health coverage of up to ₹5 lakh to over 410 million families.
PMGKAY (Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana): Free food grains are being provided to 800 million people.
Stand-Up India and PM Vishwakarma Yojana: These schemes provide loans and training to SC/ST communities and women to support entrepreneurship.
Due to the effective implementation of these schemes, between 2011 and 2023, around 171 million people rose above the poverty line, and the poverty rate in the country fell from 16.2% to 2.3%.
Question 4: What does this mean for the common people?
Answer: This means that more people in India are now in a better economic position. Compared to earlier, more families are getting access to food, healthcare services, banking, and employment opportunities.
The data shows that the benefits of India's economic growth are not limited to the rich, but are reaching all sections of society. In a way, this is India's model — a potential example for the world — showing that economic growth and social equality can go hand in hand.
Question 5: Are there any challenges that still remain?
Answer: Yes, in a large and diverse country like India, inequality still exists in certain regions and communities. Significant economic differences can still be seen between rural and urban areas, and among various states. However, the World Bank report shows that India is moving in the right direction.
Question 6: Is this news completely reliable?
Answer: This news is based on the World Bank's 2025 report and data provided by India's Ministry of Social Welfare. However, the Gini Index only reflects income distribution and does not fully capture other aspects of social inequality, such as access to education or healthcare.
Disclaimer: All the information provided in this article is based on details available on the internet. We do not claim complete accuracy of any information.
0 comments:
Post a Comment